Overview
The CEH certification training course in Singapore equips professionals with cutting-edge AI-powered tools and techniques to excel in ethical hacking. This advanced course covers every phase of ethical hacking, from reconnaissance and scanning to maintaining access and securing systems. Leveraging AI integration, participants will learn to automate threat detection, predict potential breaches, and swiftly respond to cyber incidents. Additionally, the course focuses on securing AI-driven technologies, empowering organizations to stay resilient against evolving threats.
The CEH certification integrates practical experience and a structured approach to ethical hacking methodologies. By combining ethical hacking expertise with advanced AI capabilities, participants gain the skills needed to conduct proactive threat hunting, anomaly detection, and predictive analysis. This certification not only deepens your understanding of system vulnerabilities but also prepares you to strengthen security measures, reducing the risk of cyber-attacks and ensuring robust organizational defenses.
Course Description & Learning Outcomes
CEH provides the most extensive, immersive hands-on lab and practice range experience in the market, along with a thorough training program designed to prepare you for the certification exam.
What You Will Learn ?
- Leverage AI-driven techniques to enhance your ethical hacking skills, automate threat detection, predict breaches, and stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
- Key issues plaguing the information security world include ethical hacking, information security controls, laws, and standards.
- Conduct foot printing and reconnaissance utilising cutting-edge techniques and tools as an essential pre-attack phase required in ethical hacking.
- Network scanning countermeasures and techniques.
- Enumeration countermeasures and techniques.
- Conducting vulnerability analysis, which involved identifying security weaknesses within the network, communication infrastructure, and end systems of the target organization.
- Unveiling system and network weaknesses using techniques such as steganalysis attacks, system hacking methodology, covering traced and steganography.
- Social engineering techniques and how to identify theft attacks to audit human- level vulnerabilities and suggest social engineering countermeasures.
- DoS/DDoS tools and attack techniques to audit a target and DoS/DDoS countermeasures.
- Various forms of malware (such as Trojans, viruses, worms, etc.), conducting system audits to detect malware attacks, analysing malware, and implementing countermeasures.
- Countermeasures, session hijacking techniques to uncover session management at network-level, authentication/authorisation, and cryptographic weaknesses.
- Packet sniffing techniques to discover network vulnerabilities and countermeasures to defend sniffing.
- Assessing vulnerabilities in web applications involves utilizing a comprehensive web application hacking methodology to identify web application attacks and implementing appropriate countermeasures.
- Countermeasures, injection detection tools to detect SQL injection attempts, and SQL injection attack techniques.
- Web server attacks and a comprehensive attack methodology to audit vulnerabilities in web server infrastructure, and countermeasures.
- IDS, honeypot and firewall evasion techniques, evasion tools and techniques to audit a network perimeter for weaknesses, and countermeasures.
- Attack vectors on mobile platforms, exploits targeting Android vulnerabilities, and guidelines along with tools for enhancing mobile security.
- Discover potential risks targeting IoT and OT platforms and acquire strategies for securely safeguarding IoT and OT devices.
- Wireless encryption, wireless hacking tools, wireless hacking methodology, and Wi-Fi security tools.
- Penetration testing, security audit, vulnerability assessment, and penetration testing roadmap.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), cryptography ciphers, cryptanalysis tools, and cryptography attacks.
- Cloud computing concepts (Server less computing, container technology), various threats/attacks, and security techniques and tools.
Course Outline
Module 01: Introduction to Ethical Hacking
Module 02: Foot printing and Reconnaissance
Module 03: Scanning Networks
Module 04: Enumeration
Module 05: Vulnerability Analysis
Module 06: System Hacking
Module 07: Malware Threats
Module 08: Sniffing
Module 09: Social Engineering
Module 10: Denial-of-Service
Module 11: Session Hijacking
Module 12: Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypot
Module 13: Hacking Web Servers
Module 14: Hacking Web Applications
Module 15: SQL Injection
Module 17: Hacking Mobile Platforms
Module 18: IoT and OT Hacking
Module 19: Cloud Computing
Module 20: Cryptography
The objective of this funded CEH course is to assist you in becoming a master of ethical hacking methodology that can be used in an ethical hacking or penetration testing situation. Our expert-led, funded programs can elevate your cybersecurity journey. With online flexibility and comprehensive content, become a certified ethical hacker ready for any penetration testing scenario, all through our convenient online training courses.
At the end of this course, you will be prepared for EC-Council Certified Ethical Hacker exam 312-50.
For more information, please click here.
Recommended Prerequisites
No prerequisites required for this course.
Who should attend?
- System Administrators
- Network Administrators and Engineers
- Web Managers
- Auditors
- Ethical Hackers
- Security Professionals in General.
Schedule
End Date: 30 Jun 2025, Monday
Duration: 5 Days, 36.25 hours Timing: 9am - 5.15pm
Location: OnlinePricing
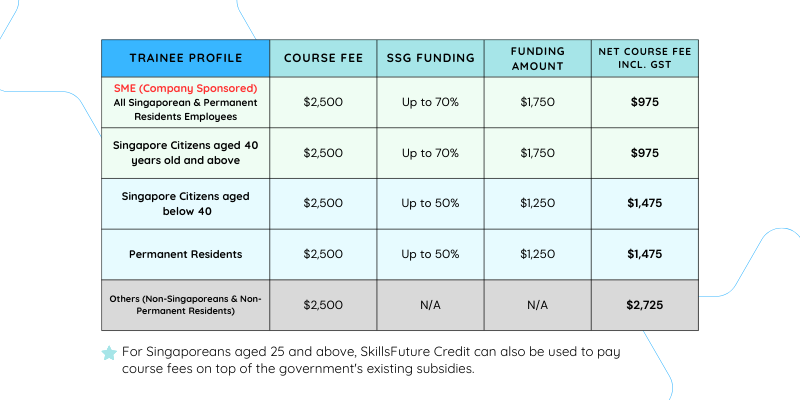
Course fees: If you meet the eligibility criteria, course fees can be subsidised by up to 70%. Moreover, SkillsFuture Credit can be applied to cover course fees in addition to existing government subsidies.
Skills Covered
PROFICIENCY LEVEL GUIDE
Beginner: Introduce the subject matter without the need to have any prerequisites.
Proficient: Requires learners to have prior knowledge of the subject.
Expert: Involves advanced and more complex understanding of the subject.
- Cybersecurity (Proficiency level: Proficient)